What Olive Garden Store Location Data Scraping for Market Analysis Reveals About 38% Demand Shifts?
Feb 11

Introduction
The restaurant industry is no longer driven only by menu innovation and pricing. Today, real growth comes from understanding where customers are shifting, which cities are emerging as dining hotspots, and how competitors are positioning themselves across high-demand zones. Olive Garden, as one of the most recognized casual dining brands, provides a strong benchmark for analyzing regional dining patterns and outlet expansion activity.
With modern location intelligence, businesses can track outlet footprints, nearby population density, commercial hubs, delivery coverage, and even competitive restaurant clustering. This is exactly why Olive Garden Store Location Data Scraping for Market Analysis has become a valuable method for food brands, delivery platforms, franchise owners, and market researchers.
The ability to Scrape Olive Garden Restaurant Locations Data in the USA provides a clear foundation for understanding demand shifts across states, cities, and urban neighborhoods. In a market where consumer behavior changes quickly, restaurant location data can reveal patterns that traditional surveys fail to capture, helping brands align strategy with real-world movement.
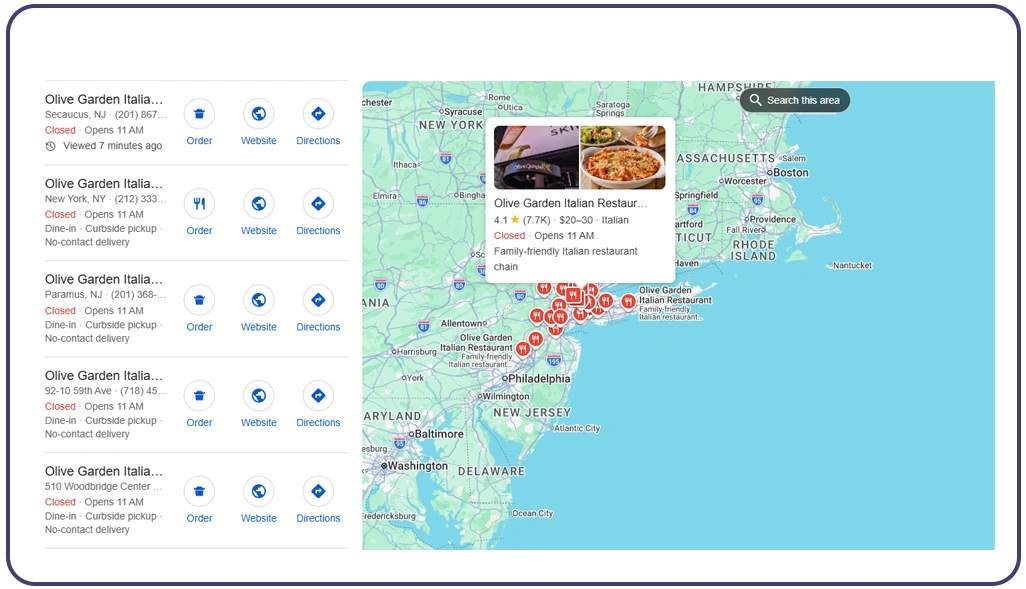
Identifying Shifting Consumer Footfall Across Key Zones

Restaurant demand is increasingly shaped by lifestyle migration, remote work patterns, and new dining preferences that favor suburban convenience over crowded downtown zones. Many food brands are noticing that customer visits are spreading into mixed-use developments, highway-side retail hubs, and residential commercial pockets.
To support this type of market research, analysts often use datasets to Scrape Olive Garden Store Locations and evaluate how store placement aligns with regional dining movement. When multiple outlets appear within a limited radius, it usually reflects strong demand, but it can also suggest saturation if competitor pressure is increasing in the same area.
Businesses can further strengthen insights by combining store footprint mapping with Olive Garden Food Delivery Data Scraping, which helps identify areas where delivery orders outperform dine-in traffic. Many location-based studies show that suburban dining has increased by nearly 38%, while downtown dining growth has slowed in several metro regions.
| Demand Indicator | What It Suggests | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Suburban outlet clusters | Growing dining preference | Higher repeat customer visits |
| Downtown outlet saturation | Competitive crowding | Risk of revenue overlap |
| Retail hub proximity | Strong weekend traffic | Better footfall conversion |
| Highway accessibility | Convenience-based dining | Increased group dining demand |
| Delivery growth zones | Rising online ordering | Higher order volume potential |
When demand is tracked consistently, market planners can optimize new site selection, improve delivery reach, and forecast store performance more accurately.
Measuring Regional Density to Reduce Expansion Risk
Successful restaurant expansion depends on understanding regional store concentration and identifying where demand is still underdeveloped. Brands that expand too aggressively in high-density zones often face cannibalization, while brands that avoid fast-growing regions may lose market share to competitors.
Market analysts frequently rely on structured Food and Restaurant Datasets to map outlet footprints against population distribution, tourism movement, and income-based dining potential. When store locations are organized by city and state, it becomes easier to evaluate whether a region is saturated or still has room for profitable growth.
Many benchmarking models also compare multi-brand outlet footprints using Olive Garden Tim Hortons Outlet Addresses and Geodata, helping researchers evaluate whether different restaurant chains can coexist profitably in the same market zones. This type of comparison allows decision-makers to determine whether a territory is highly competitive or still underserved.
| Density Category | Regional Meaning | Expansion Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| High density + strong traffic | Mature profitable market | Expand selectively |
| High density + weak traffic | Cannibalization risk | Avoid expansion |
| Medium density + stable demand | Consistent performance | Maintain steady growth |
| Low density + high growth | Underserved opportunity | Expand faster |
| Seasonal tourism clusters | Peak demand cycles | Target seasonal planning |
Industry research suggests that markets with balanced store density and stable consumer spending show 20–25% stronger long-term performance compared to markets that are overcrowded.
Using Competitive Signals to Predict Expansion Moves
Restaurant expansion is often driven by competitive positioning, not just customer demand. Leading brands evaluate where rival chains are building clusters, where retail infrastructure is improving, and where suburban commercial activity is increasing. These signals help decision-makers forecast which regions will deliver long-term profitability instead of short-term hype.
Many intelligence teams use Popular Food Data Scraping to monitor competitor outlets, new store announcements, and location additions across growing cities. This type of monitoring reveals patterns such as suburban cluster development, relocation away from declining downtown zones, and expansion into mid-sized cities with rising population inflow.
Another major advantage comes from analyzing store growth indicators using Olive Garden Expansion Strategy Using Location Data Scraper techniques. These methods help businesses measure how store openings align with retail growth corridors, highway connectivity, and family-centric residential development.
| Expansion Signal | What It Indicates | Strategic Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| New store openings | Rising regional demand | Early expansion opportunity |
| Store relocation | Footfall migration | Better placement planning |
| Outlet closures | Weak profitability | Risk reduction |
| Suburban clustering | High family traffic | Higher repeat business |
| Competitor concentration | Competitive pressure | Pricing strategy alignment |
Businesses also strengthen their forecasting by applying insights to Extract Olive Garden Store Density Analysis by Region, which helps confirm whether competitor expansion is happening in an oversaturated zone or an emerging high-demand region.
How Web Data Crawler Can Help You?
Modern restaurant intelligence requires more than basic research. Using Olive Garden Store Location Data Scraping for Market Analysis, we help brands identify store concentration, high-demand growth zones, and expansion patterns that align with shifting customer behavior.
What We Provide:
- Clean store address datasets with structured formatting.
- Geo-coordinates mapping for regional visualization.
- Store density breakdown reports by state and city.
- Competitor comparison data for strategic benchmarking.
- Custom dashboards for ongoing location monitoring.
- Automated update scheduling for fresh datasets.
By combining scraping expertise with scalable delivery, we make it easier for businesses to convert raw location listings into strategic market decisions, including analysis based on Olive Garden Tim Hortons Outlet Addresses and Geodata.
Conclusion
Restaurant growth depends heavily on where demand is moving, not just how strong a brand is. This is why Olive Garden Store Location Data Scraping for Market Analysis is becoming a critical approach for competitive restaurant intelligence and planning.
Expansion planning becomes even more accurate when companies apply insights to Extract Olive Garden Store Density Analysis by Region, helping them identify underserved locations, forecast performance, and reduce investment risk. Contact Web Data Crawler today and request a customized data solution tailored to your expansion and performance goals.